Due to my Samsung Galaxy Watch starting to become very erratic with accurate tracking of my heart rate during exercises (I get bonus rewards that depend on that data) I opted to buy a Polar H10 Chest Strap this last week.
But although the chest strap data is super accurate, it was only registering with the Polar Beat app through to my medical insurance. I could not get it to show inside Samsung Health at all. There are quite a few videos and articles on how to connect an external Bluetooth sensor, such as a chest strap, to Samsung Health but that in no way does what you expect it to do (it does nothing).
The reason is, Samsung Health defaults to using only the Galaxy Watch for heart rate monitoring (HRM) if it is connected, even if the chest strap is registered in Samsung Health as an accessory. The app has no way at all to switch between the Watch and any external device (why not Samsung?).
So, there are actually TWO different ways of getting your chest strap data into Samsung Health. Just very important to note that the single Bluetooth channel between the phone and the chest strap, can only be managed by ONE app at a time, so you must choose to either use Samsung Health or the Polar app.
Samsung Health App with Polar H10 Chest Strap* Make sure the Polar app or other app is not using the chest strap.
* Make sure you have added the chest strap as an external accessory inside Samsung Heath app -> three dots menu / Accessories / Scan for Accessories
* Go to the Galaxy Wearable app and disconnect the Watch. No need to unpair the Bluetooth.
* You must start an exercise from the Samsung Health app, and not from the Watch itself. If you start it from the Watch, it will record using the Watch HRM sensor.
* In the Samsung Health app, tap on the exercise symbol you want to use to open the start exercise screen. The small green symbol at the top left indicates what HRM sensor is going to be used. If the one for the external device is shown (cross-link chain), you can go ahead and start your exercise by tapping on the start button.
* Remember EACH time to disconnect the Watch before starting any exercise.
Using StravaYou could either just use the Strava app as your primary exercise app (with the chest strap linked to that app directly), or like I’m doing, I’m using the Polar Beat app with the chest strap and the Polar app is configured to push the exercise data to Strava.
The important thing that must be done though, is inside the Samsung Health app, you need to connect it to the Strava service.
* First ensure you do have the Strava app installed, and you have linked it / created your Strava account.
* To link the Samsung Health app to Strava: Click on the three dot menu to go to Settings / Services / Toggle on Strava connection.
Now you can use either the Strava app or the Polar Beat app. Inside Samsung Health you should then see the exercise appear with the Strava tag on it. In my case it still showed the Watch exercise too, as I had recorded with both. But I deleted the Watch exercise and Samsung Health still counts in the Strava exercise in its stats and shows the HR graph etc if you open it.
With the Strava option it is better NOT to start any exercise on the Watch, nor inside the Samsung Health app, just so you don’t end up with duplicate workouts shown inside Samsung Health. You may also want to disable auto-recognition of exercises in the Galaxy Wearable app for the Watch as well.
Original post at
How to get Polar H10 Chest Strap (or other external Bluetooth sensors) data into Samsung Health for Workouts#
technology #
health #
PolarH10 #
SamsungHealth #
workouts 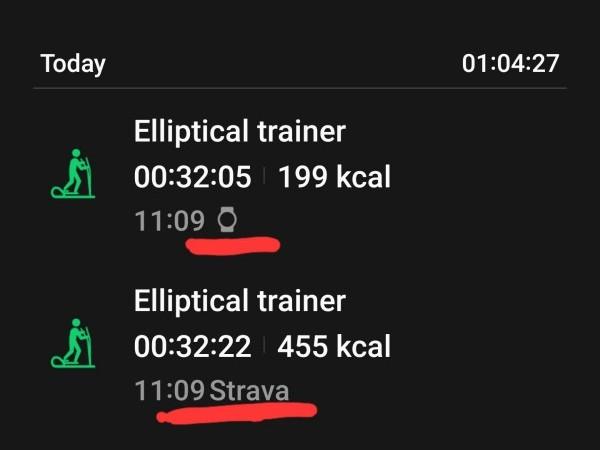
Due to my Samsung Galaxy Watch starting to become very erratic with accurate tracking of my heart rate during exercises (I get bonus rewards that depend on that data) I opted to buy a Polar H10 Chest Strap this last week. But although the chest strap data is super accurate it was only registering with...
